T. Musapelo, K.K. Murray, “Particle formation by infrared laser ablation of MALDI matrix compounds,” J. Mass Spectrom. 49 (2014) 543–549. doi:10.1002/jms.3378.
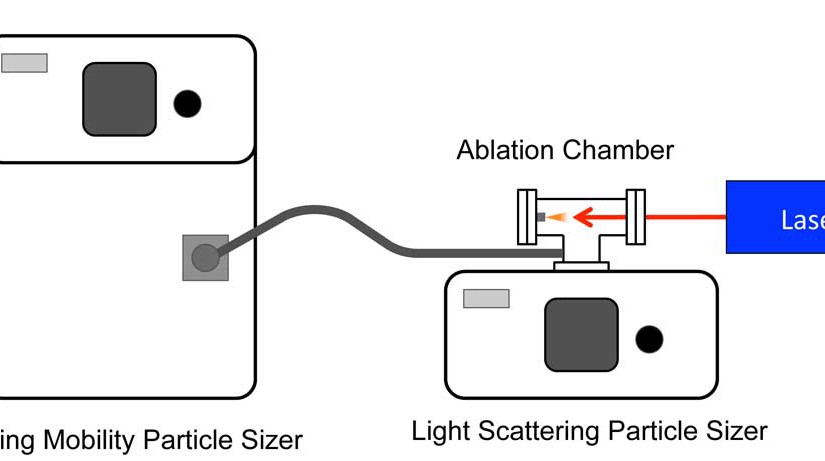
Abstract: The concentration and size distribution of particles ablated from the infrared matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization matrix compounds succinic acid (butanedioic acid), α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid, and glycerol were measured using an aerodynamic particle sizer combined with a scanning mobility particle sizer. The two sizing instruments together had a sizing range to from 10 nm to 20 µm. Thin layers of the matrix compounds were irradiated with fluences between 6.0 and 9.5 kJ/m(2) and wavelengths between 2.8 and 3.0 µm. The distribution of particles was characterized by a large concentration of clusters in the 20-nm-diameter range and large component of mass in the range of coarse particle with diameters greater than 1 µm. The wavelength dependence revealed a blue shift for the maximum particle production that is attributed to heating and disruption of the hydrogen bonds in the matrix that shifts the absorption to shorter wavelengths. This blue shift has been observed previously in infrared matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization.