X. Fan, K.K. Murray, “UV laser irradiation of IR laser generated particles ablated from nitrobenzyl alcohol,” Appl. Surf. Sci. 255 (2009) 6297–6302. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.02.005.
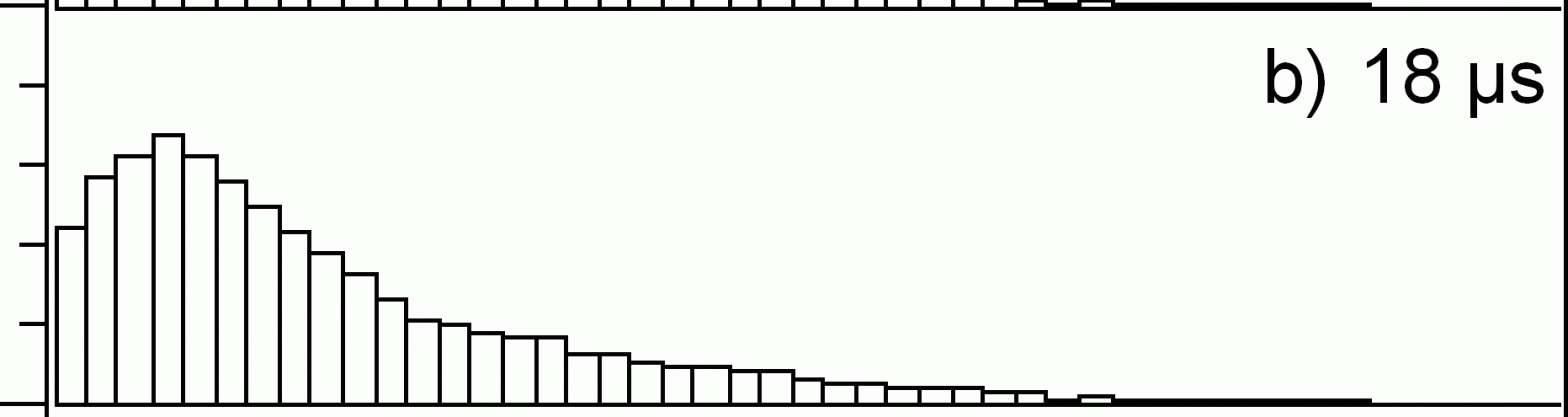
Abstract: Particles generated by 2.94 µm pulsed IR laser ablation of liquid 3-nitrobenzyl alcohol were irradiated with a 351 nm UV laser 3.5 mm above and parallel to the sample target. The size and concentration of the ablated particles were measured with a light scattering particle sizer. The application of the UV laser resulted in a reduction in the average particle size by one-half and an increase in the total particle concentration by a factor of nine. The optimum delay between the IR and UV lasers was between 16 and 26 µs and was dependent on the influence of the IR laser: higher influence led to a more rapid appearance of particulate. The ejection velocity of the particle plume, as determined by the delay time corresponding to the maximum two-laser particle concentration signal, was 130 m/s at 1600 J/m^2 IR laser influence and increased to 220 m/s at 2700 J/m^2. The emission of particles extended for several ms. The observations are consistent with a rapid phase change and emission of particulate, followed by an extended emission of particles ablated from the target surface.